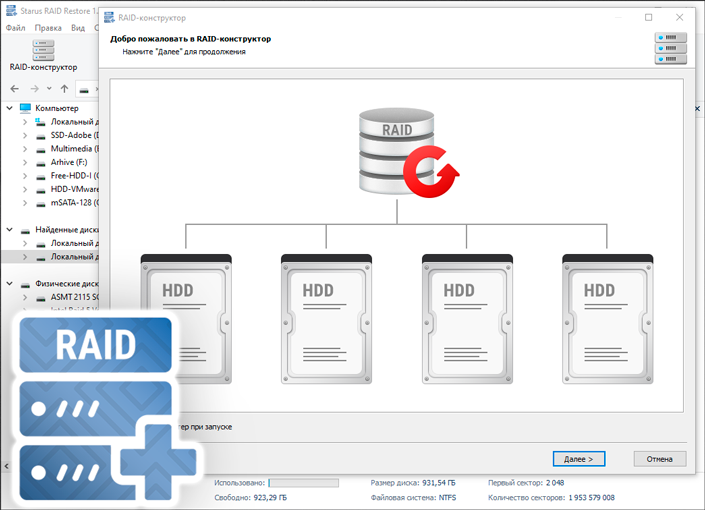
Starus RAID Restore supports all popular controller types and works with the following types of arrays:
- Basic: RAID 0 / 1 / 4 / 5 / 6
- Combined: RAID 01 / 10 / 50 / 60 / 1E / 5E / 5EE
In addition to the basic purposes, Starus RAID Restore supports single-drive volumes and JBOD composite arrays. In addition, the application is also compatible with software controllers such as Storage Spaces.
Causes of RAID damage
No device just breaks down. It must be preceded by a number of possible causes. Let’s look into them.
- Disc damage.
Perhaps the most common reason. Hard disks and SSDs cannot last forever, they both have a very limited lifespan, which over time risks being used up. Of course, for server disks like NAS or SCSI, this lifespan is much higher, but let’s not forget that nothing in this world lasts forever. For most RAID arrays, the loss of even a single disk can be fatal – one failure and all devices fail like a chain reaction. Therefore, disk corruption is the leading cause of all array failures. - Damage or failure of the controller.
If you damage the engine in a car, it won’t go anywhere. It’s the same with RAID arrays. If the controller is damaged, it needs to be replaced immediately. A RAID controller is a virtualization technology that combines several physical disks into one logical module. This helps improve fault tolerance and performance. If the controller gets damaged, the array fails. - Damage or failure of the motherboard.
If the user can not buy a hardware controller, he creates a software controller, directly on the motherboard. Its failure, BIOS firmware update, power surge or wrong connection of the disks – all these can cause damage to the array. It can only be restored by recreating it. - Damage to the operating system.
Software RAID arrays created within Windows, MacOS, Linux, Ubuntu and FreeBSD are directly dependent on the performance of the operating system. Any incorrect driver or OS update can cause an array to fail irreparably. Consequences can range from a startup error to complete loss of stored information. - Recreating an array.
RAID can fail not only due to software or hardware failures, it can also occur due to human error. Replacing a disk in an array, recreating instead of rebuilding, connecting disks in the wrong order – all of these errors can lead to a guaranteed failure. After them the RAID will not be able to recover on its own. - Viral attack.
Regardless of which controller (software or hardware) your RAID array is running on, it can fall victim to a virus attack. Malicious software can easily corrupt system files, disable the operating system, modify the partition table and create a number of other critical failures. Without manual intervention, RAID will not be able to recover from such errors. - Damage to disk sectors.
All disks work on the principle of ignoring damaged sectors by writing information about their failure to a special table. However, in RAID arrays the situation changes dramatically when an entire disk fails at once. In this case it is necessary to replace the disk urgently and not to turn on the array until the repair is completed. - System or hardware upgrades.
Some manufacturers do not allow you to upgrade to new hardware without reorganizing the existing RAID array. The only way to avoid losing data in this situation is the “Ctrl + C, Ctrl + V” method. You will have to copy the necessary files of the old raid and then install them into the new one. - Incompatibility.
If the hard disk is running in RAID A, you cannot install it in RAID B. Otherwise service information will be overwritten and such incompatibility when reconnecting may cost you files. The array will be damaged and you will have to recreate it.
Features of Starus RAID Restore
RAID Restore is versatile and offers extensive RAID capabilities. Fix array errors, recover and export lost files. And the handy preview window makes the process fun and easy. Because now you always know exactly what you’re recovering from the disk.
RAID Builder
Recovering RAID arrays is a difficult task and can only be done by experienced engineers with years of experience. We decided to change that. Now even inexperienced users can bring a hard drive array back to life.
Auto mode
The default application mode.
In automatic mode Starus RAID Restore prompts user to select names of disks installed in the array. Then the program switches to analysis mode and checks all possible RAID combinations that can be installed on the specified number of devices.
Once the application determines what arrays can be created on your hardware, it will start diagnosing the structure of the file system: logical partitions, directory tree and files. This type of analysis is useful in situations when the user does not know the block size and RAID type of his PC.
Search by controller manufacturer
The program offers a whole set of presets to work with. You don’t have to google anything or manually type in the names, where there’s always the risk of a typo. Simply select the desired system, RAID type and start the recovery process.
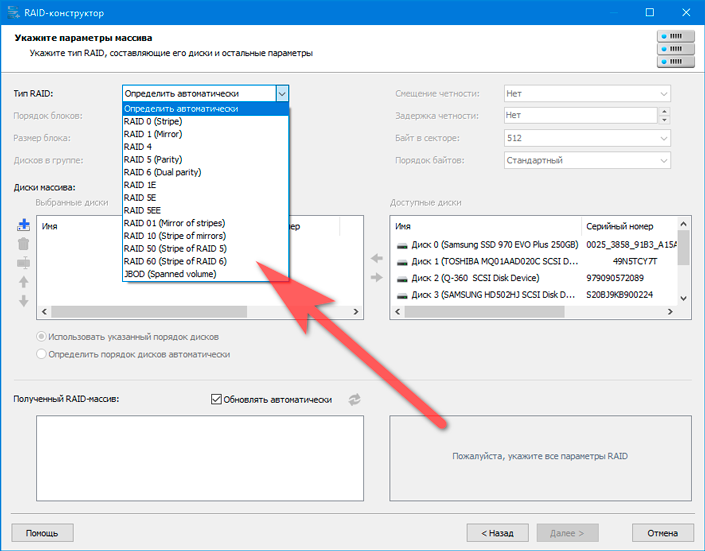
Restore RAID in manual mode
Manual RAID mode offers to create an array with any parameters. You can select the RAID type, block order, block size, delay, and explore the RAID block diagram in the lower right corner.
Please note! This mode is suitable only for experienced users. If you are unsure of the data you are entering, it is better to select RAID creation/rebuilding in automatic mode or in preset mode.
Supported RAID levels:
Starus RAID Restore supports arrays created both software and hardware (using special controllers).
- JBOD is a sequential writing scheme. It works on the following principle: as soon as the first disk runs out of free space, the array moves on to the second, third and so on. Very similar to the standard hard disk operation, only this time a huge;
- RAID 0 – works on an interleaved basis. Blocks of data are written alternately on all disks. Array is used to increase memory capacity and data access speed. Requires a minimum of 2 disks;
- RAID 1 – works on the principle of mirroring. The array duplicates the data of the first disk to the second disk. So if files on one of the devices are compromised due to corruption, you can always restore them intact on the second drive. A minimum of 2 disks is required;
- RAID 10 (1+0) – at least 4 disks are required;
- RAID 1E (1 + 0 shifted) – Minimum 3 disks required;
- RAID 5 – works on the principle of alternation with the preservation of the checksum. The advantage of this array is that it can restore itself after a failure of 2 disks. Increases system performance, expands storage capacity and protects files from loss. Requires a minimum of 3 disks;
- RAID 50 (5 + 0) – at least 6 disks required;
- RAID 5E and RAID 5EE (Layer 5 analog with a spare disk in case of failure) – Requires a minimum of 4 disks;
- RAID 6 – operates on the principle of alternating with the preservation of two checksums and uses the Reed Solomon code. The advantage of the array is that it can self-repair after a corruption of 2 disks in the system. Used to increase storage capacity, improve read and write speeds, and ensure storage reliability;
- RAID 60 (6 + 0) – requires a minimum of 8 disks;
- RAID 2 – used to combine two groups of data disks for error correction. Uses Hemming code and is used for multi-disk arrays. Requires a minimum of 3 disks;
- RAID 3 is analogous to Layer 5, but instead of alternating with all disks, the checksum is always written to only one of them. Uses 1-byte blocks;
- RAID 4 is analogous to RAID 3 with the only difference. The block size can now be larger than 1 byte.
Supported manufacturers
Creating a virtual disk
When working with damaged discs that contain bad sectors, there is always a risk to provoke complete loss of files due to overwriting or further “crumbling”. Therefore it is recommended to create a virtual disk image before proceeding with recovery works.
By creating such an image you can be 100% sure that both the array and the data on it can be restored successfully. Starus RAID Restore supports the following images: *.dsk, *.hdd, *.vhd, *.vdi, *.vhdx, *.vmdk.
File recovery
The program finds files even on disks with a destroyed file system. While scanning, RAID Restore finds: boot sector, partition table, directories and logs with information about the files stored on the disk. Using the information found, the program recreates lost documents and allows you to export them to the disk in their entirety.
Note: Only export files to the working drive to avoid overwriting the data.
Supported file systems
RAID Restore works with the following hard drive and array file systems:
- NTFS – used on the system and ordinary disks of the Windows operating system.
- FAT/ExFAT – used on removable Flash drives and memory cards in Windows / Apple / Linux / Android.
- ReFS – used on Windows servers.
- APFS – used on Apple devices starting with MacOS High Sierra version 10.13 and later.
- HFS+ – used on iMacs, MacBooks, MacMini and other devices.
- Ext/XFS/ReiserFS – used in Linux operating systems.
- UFS – used in Solaris, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD.
Supported operating systems
Starus RAID Restore is designed to work inside a Windows operating system. To restore data from a computer running on another operating system, you will need to connect it to the main Windows device. In addition, the application also supports Windows servers: Server 2019 / 2016 / 2012 / 2008 / 2003 / 2000.

I recommend all users of RAID arrays to familiarize themselves with the Starus RAID Restore tool. It helped me rebuild the array from physical disks and quickly resurrect the data.